Data Broadband Access Equipment: The Backbone of Modern Connectivity
In today’s interconnected world, the demand for high-speed internet access is greater than ever. From streaming video content and online gaming to remote work and telemedicine, reliable and fast internet connectivity is crucial for everyday life. At the heart of this connectivity is data broadband access equipment, the technologies and infrastructure that enable high-speed internet to reach homes, businesses, and devices. These systems are the unsung heroes behind our seamless digital experiences, ensuring that data travels efficiently and reliably from the internet service provider (ISP) to end users.
Broadband access refers to the high-capacity transmission technologies that provide fast, high-volume data transmission, enabling services such as high-definition video streaming, cloud computing, and high-speed internet browsing. The role of broadband access equipment is to connect these services to individual users by providing reliable and scalable access points.
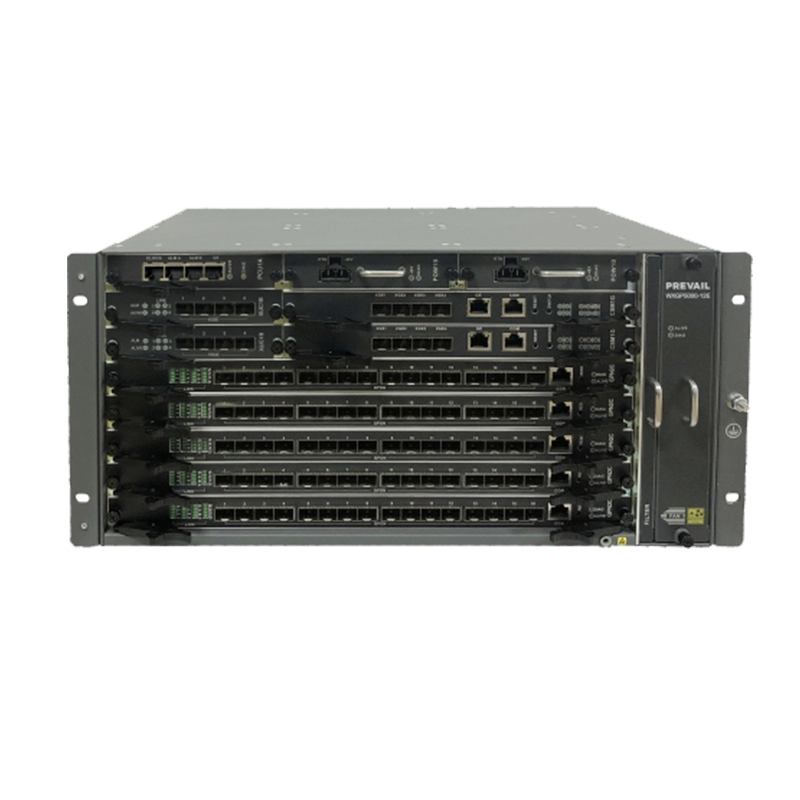

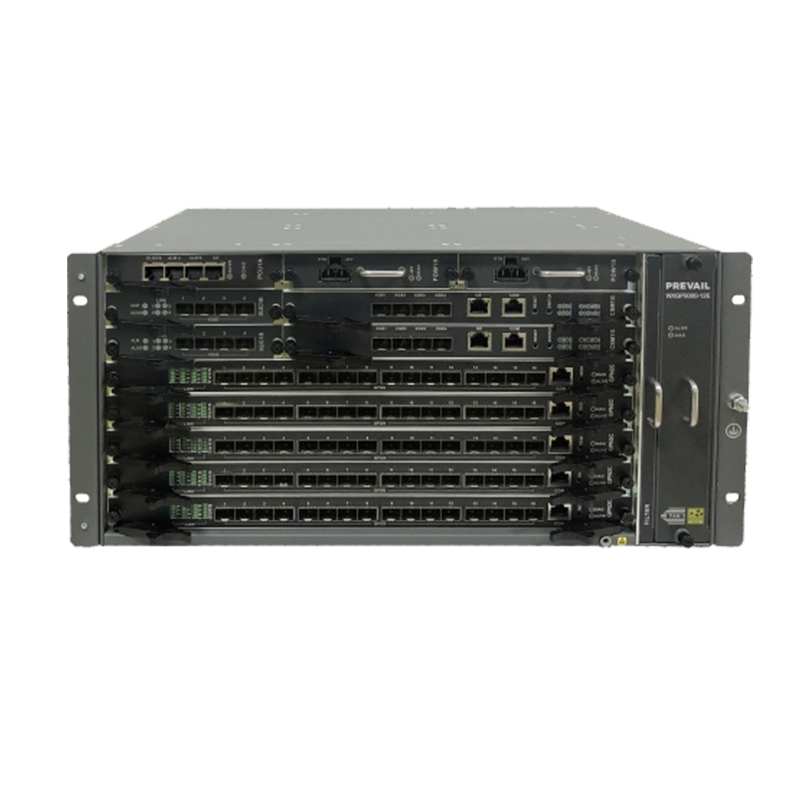
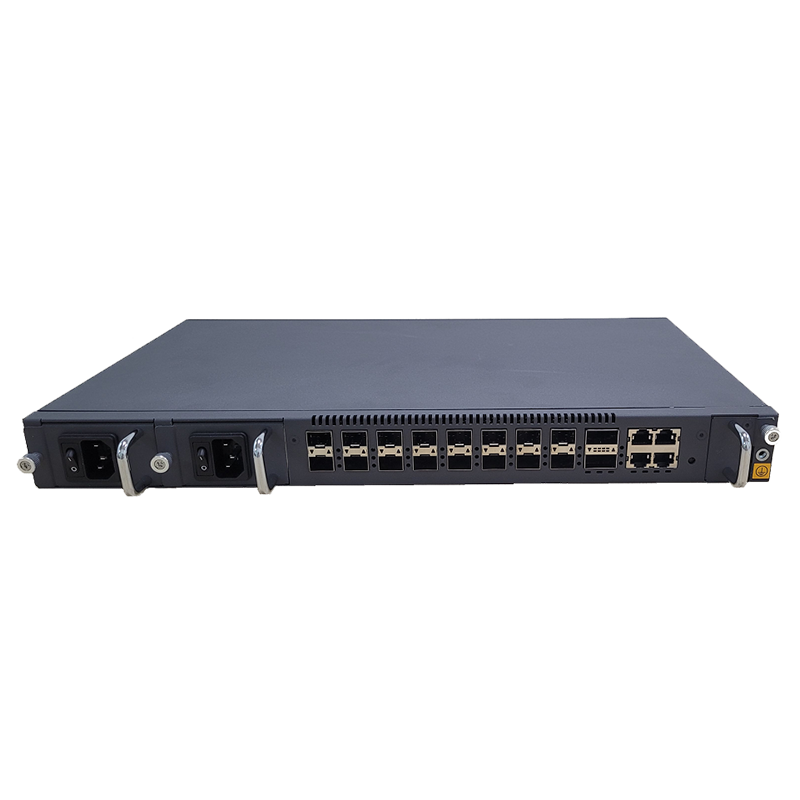
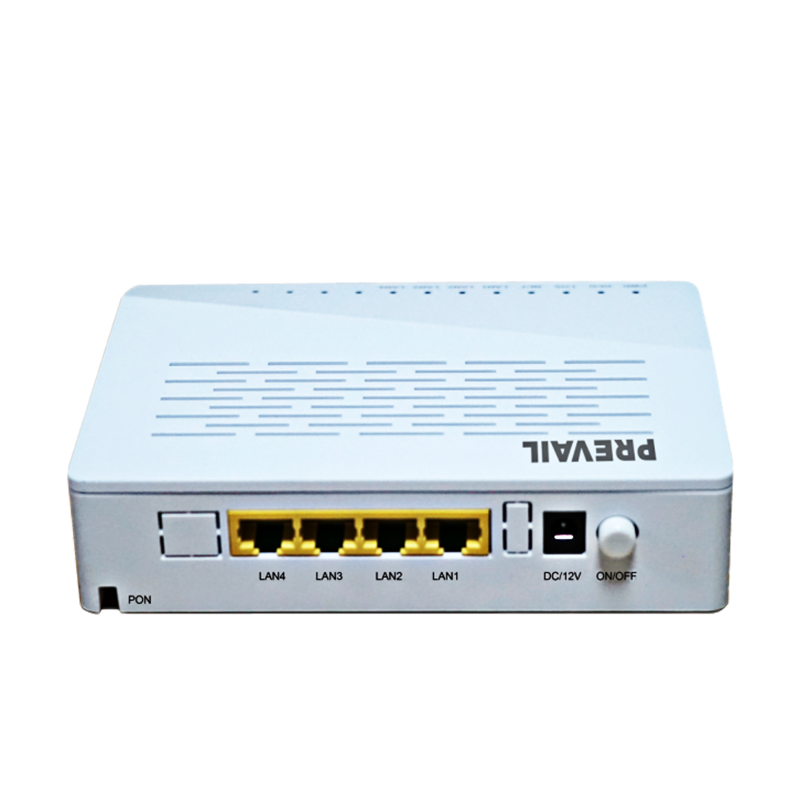
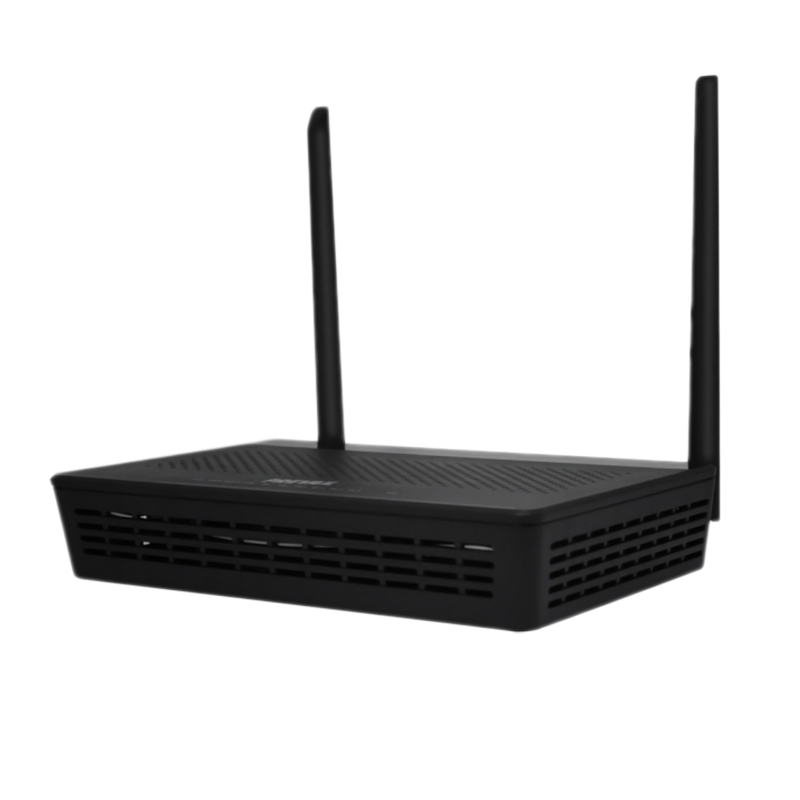
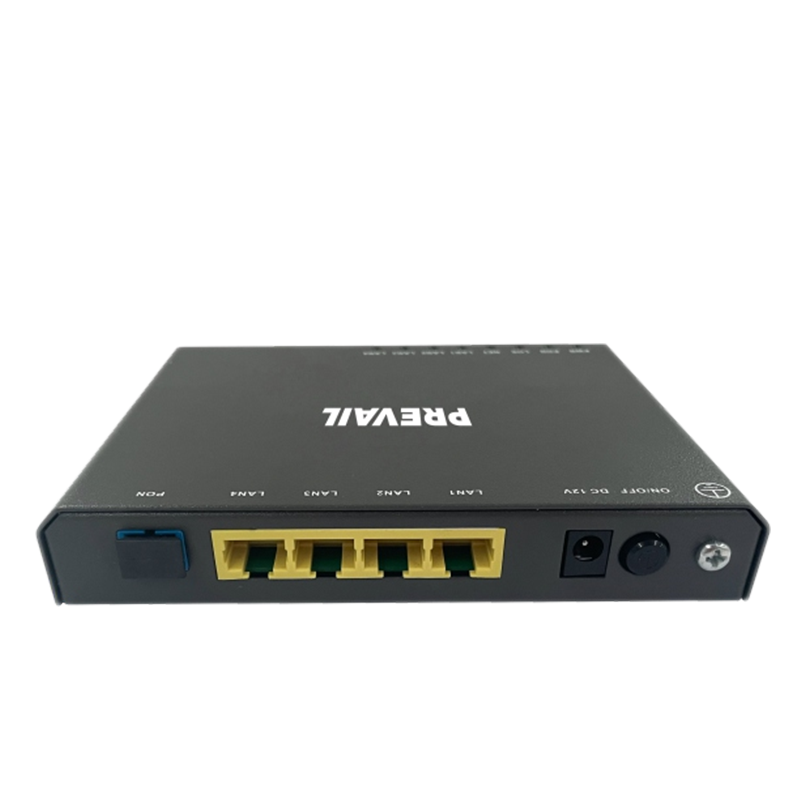
Broadband access equipment typically includes routers, modems, optical network terminals (ONTs), customer-premises equipment (CPE), and network switches. These devices work together to ensure that data flows from the service provider’s core network to the end user’s devices.
Broadband access technology has evolved over the years, with several different types of equipment designed for different types of networks. Below are the key categories of data broadband access equipment:
Modems are essential devices that connect a home or business to the broadband network, often serving as the point of entry for the internet connection. A modem translates the signal from the service provider’s network into a format that can be understood by devices within the premises.
Routers, on the other hand, are used to distribute the internet connection to multiple devices within a home or business. The router acts as a traffic controller, directing data to the correct devices via wired Ethernet connections or Wi-Fi.
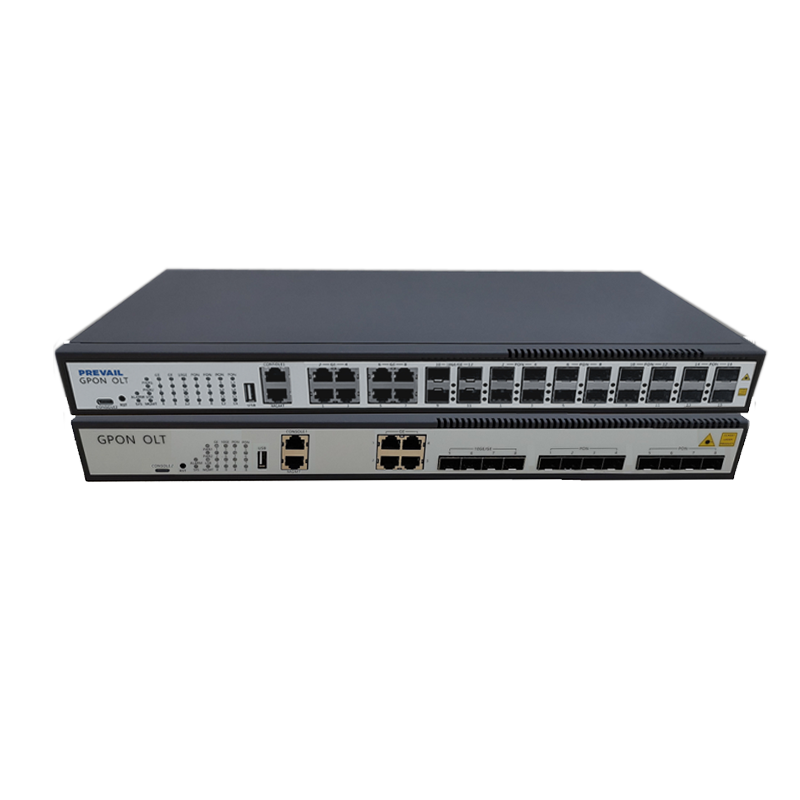
For fiber-optic broadband services, ONTs serve as the bridge between the fiber-optic network and the customer’s premises. The ONT converts optical signals sent over fiber cables into electrical signals that can be used by standard broadband equipment like routers and computers. ONTs are crucial for fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) services, ensuring high-speed data transfer and reliability.
CPE is a broad term that refers to the devices located at the customer’s premises, such as modems, routers, switches, and other equipment that enable internet access. These devices are responsible for receiving, processing, and transmitting data over the broadband network. CPE can vary greatly depending on the type of broadband service (DSL, cable, fiber, etc.) and the needs of the customer.
Network switches are used to connect multiple devices within a local area network (LAN), allowing them to communicate with each other and share resources. Switches are often deployed in business environments to manage data traffic and ensure the efficient use of broadband resources. In residential networks, hubs or simpler routers may be used for connecting devices.
Gateways combine the functionalities of a router, modem, and sometimes even a switch or access point in a single device. Gateways simplify network setups by providing an all-in-one solution for home or business broadband access. They are commonly used in broadband networks that require simultaneous connectivity to different types of networks (e.g., combining internet access with a home security system).
Wi-Fi access points (APs) are used to extend the range of wireless internet connections within a building. These devices connect to the router via Ethernet and broadcast the Wi-Fi signal to multiple devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets. In large homes or office buildings, multiple access points may be required to ensure consistent and strong wireless coverage.
The function of data broadband access equipment is to establish and manage the data flow between users and the internet. Here’s a basic overview of how this equipment operates:
The broadband service starts with a signal from the internet service provider (ISP) to the customer’s premises. This signal could be transmitted through various mediums, such as fiber-optic cables, coaxial cables, or telephone lines. The modem or ONT receives the signal and converts it into a usable data format.
Once the signal is converted, it needs to be distributed to various devices within the home or business. This is where the router and switches come in. The router assigns IP addresses to devices on the network, allowing them to communicate with each other and the wider internet. It also manages data traffic, ensuring that each device gets the bandwidth it needs without overwhelming the network.
For wireless internet access, the router or a dedicated Wi-Fi access point broadcasts the internet signal over the airwaves, allowing devices like smartphones, laptops, and tablets to connect wirelessly. Wi-Fi protocols such as 802.11ac or 802.11ax ensure that these devices receive strong, fast internet connections.
Once the equipment is set up and connected, it enables data transfer. Whether browsing the web, downloading files, or streaming videos, data packets are sent and received through the broadband network. The equipment ensures that the data is transferred accurately, securely, and without delay.