FTTH Optical Receiver: The Backbone of High-Speed Fiber Optic Networks
Fiber to the Home (FTTH) is rapidly becoming the standard for high-speed internet delivery across the globe. As internet speeds continue to increase and the demand for reliable, high-quality connections grows, FTTH technology plays a pivotal role in providing seamless, high-bandwidth services directly to homes and businesses. At the heart of FTTH systems is the FTTH optical receiver, a crucial component responsible for converting optical signals transmitted through fiber optic cables into electrical signals that can be processed by end-user devices.
FTTH optical receivers are typically part of a larger Optical Network Unit (ONU) or Optical Network Terminal (ONT) installed in the user’s home or business. These devices serve as the final stop in the fiber optic network before data reaches the end-user device.
The operation of an FTTH optical receiver is straightforward yet highly sophisticated. Here’s how it works:
The optical receiver receives light signals transmitted via fiber optic cables from the service provider’s central office or distribution hub. These signals are modulated with data, meaning that information is encoded in the form of light pulses.
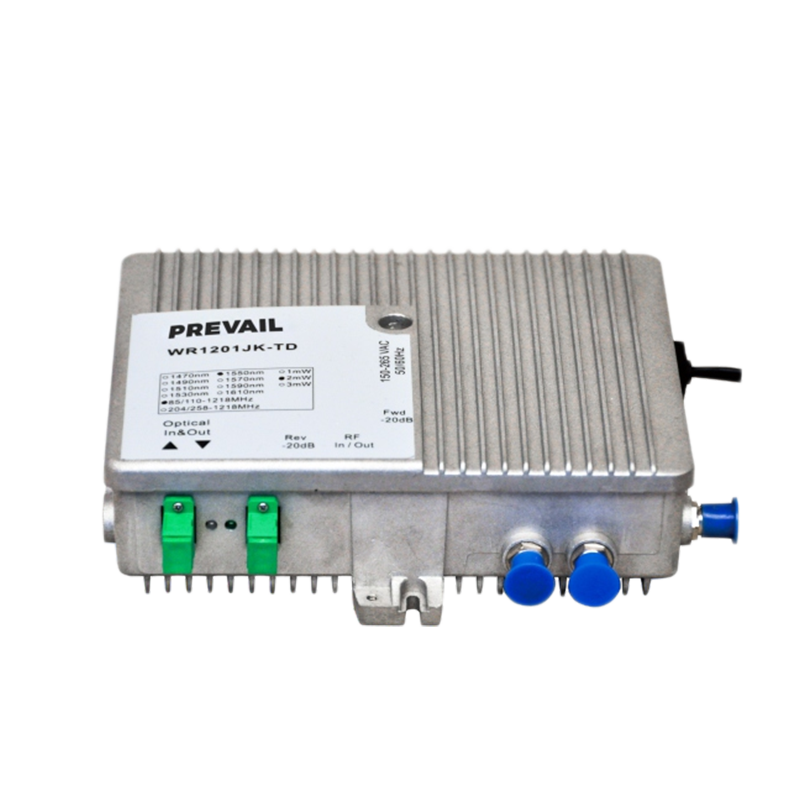

The optical receiver contains a photodetector, such as a photodiode or phototransistor, which detects the incoming light pulses. The photodetector converts these light pulses into corresponding electrical signals by exploiting the photoelectric effect. This conversion process is what enables the network to bridge the gap between optical transmission and electrical processing.
After the optical signal is converted into an electrical signal, it may be weak and in need of amplification. FTTH optical receivers often include amplifiers and signal processors to strengthen the signal before transmitting it to the end-user’s equipment. The processed signal is then sent to devices such as routers, modems, or directly to the device that requires the data.
Once the signal is properly amplified and processed, the electrical signal is routed to the end-user’s devices. Depending on the setup, the signal might be delivered over Ethernet, Wi-Fi, or coaxial cables, ensuring the user has access to high-speed internet and other services such as IPTV or VoIP.
FTTH optical receivers are designed with several key features to ensure reliable and efficient performance in fiber optic networks. Some of the most important features include:
FTTH optical receivers need to be highly sensitive to detect weak light signals that have traveled long distances through fiber optic cables. The higher the sensitivity, the better the receiver can detect low-intensity signals, improving the overall performance of the FTTH network.
In high-speed networks, reducing latency is crucial to providing seamless internet service. FTTH optical receivers are designed to have low latency, which means that the time between receiving the optical signal and delivering the data to the end-user device is minimized. This is particularly important for applications like gaming, video conferencing, and live streaming, where delays can significantly degrade user experience.
FTTH optical receivers must support high data rates to accommodate modern internet demands. As FTTH networks offer gigabit speeds and even higher bandwidth capabilities, optical receivers must be capable of handling large volumes of data, including high-definition video, cloud computing applications, and more.
Fiber optic signals are generally very reliable, but errors can still occur due to various factors such as signal degradation, noise, or interference. Many FTTH optical receivers incorporate error detection and correction features to ensure data integrity, making sure that the data received by the end-user device is accurate.
FTTH optical receivers are often integrated into an Optical Network Terminal (ONT) or Optical Network Unit (ONU), which are responsible for the entire signal processing, routing, and distribution within the home or business. These devices provide multiple outputs for different services such as internet, television, and telephone, streamlining the delivery of services to end-users.
FTTH optical receivers are vital to the overall success of fiber optic networks. Without them, the optical signals sent through fiber optic cables would remain in their light form and would not be usable by any end-user devices. As the demand for faster, more reliable internet grows, FTTH optical receivers continue to evolve, offering higher bandwidth, lower latency, and greater efficiency.
They play a key role in the ongoing shift towards fiber-based broadband services, enabling consumers and businesses to access internet speeds that were previously unimaginable with copper-based infrastructure. Additionally, FTTH optical receivers are essential in the implementation of next-generation technologies such as 5G backhaul, Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity, and smart cities.