How Do 1550nm Optical Amplifiers Enhance Long-Distance Fiber Optic Communications?
In the world of telecommunications and optical networks, 1550nm optical amplifiers play a crucial role in enhancing the performance of fiber optic systems. These amplifiers are designed to boost the signal strength in optical fibers, allowing data to travel over long distances with minimal loss and distortion. Operating at a wavelength of 1550nm, they are integral to modern communication infrastructure, such as high-speed internet, cable television, and long-haul telecommunication systems.
The 1550nm optical amplifier specifically amplifies signals at a wavelength of around 1550 nanometers, which is one of the most commonly used wavelengths in optical fiber systems. This wavelength is preferred because it lies in the telecom window of fiber optic cables, where the least amount of light loss occurs, allowing for efficient data transmission over long distances.
The most widely used types of optical amplifiers for the 1550nm wavelength are erbium-doped fiber amplifiers (EDFAs) and Raman amplifiers. These amplifiers work by using specific materials or techniques to boost the intensity of light signals, making it possible to extend the reach of optical communications.
The EDFA is the most popular and widely used optical amplifier for 1550nm signals. It works by doping a section of optical fiber with erbium ions (Er3+), which have special properties that allow them to absorb energy from a pump laser and then release this energy in the form of amplified light. The process involves the following steps:
A pump laser (usually at 980nm or 1480nm) excites the erbium ions within the fiber.
The excited erbium ions then transfer their energy to the incoming signal light (at 1550nm).
This energy transfer results in the amplification of the signal, which is then transmitted further along the fiber.
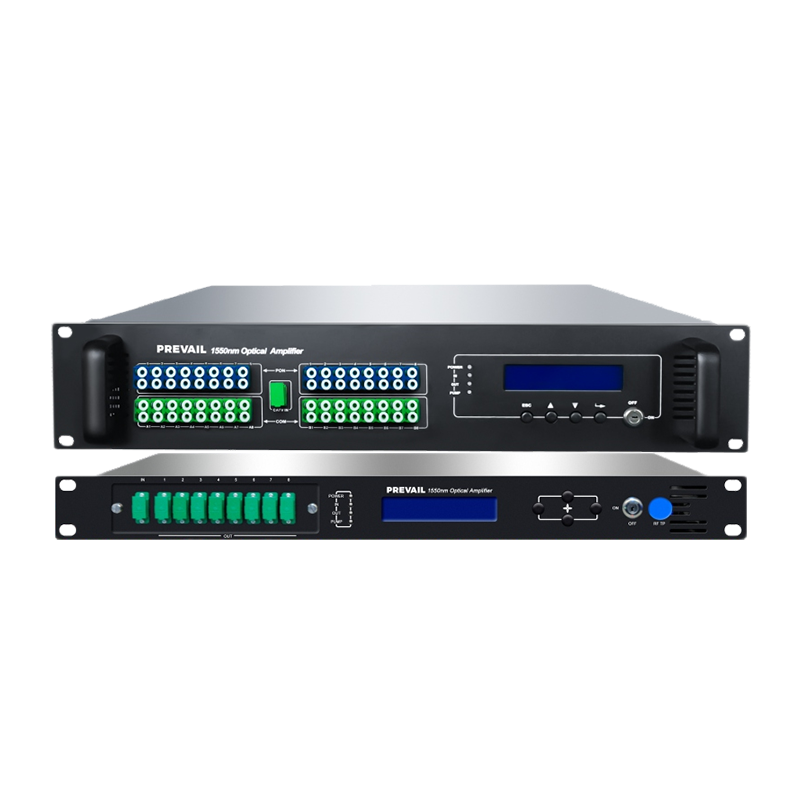

EDFAs are known for their high efficiency and low noise levels, making them ideal for long-haul optical networks.
Raman amplifiers work based on the Raman scattering effect, where a portion of the signal’s power is transferred to other optical modes through interaction with the fiber. In this type of amplifier, the light signal is boosted by transferring energy from a pump signal. Raman amplification can provide higher gain across a wide range of wavelengths and is particularly useful when combined with EDFAs in wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) systems.
One of the primary advantages of 1550nm optical amplifiers is their ability to maintain signal strength over long distances. In traditional optical systems, signal loss increases as the signal travels farther down the fiber, requiring frequent regeneration. However, optical amplifiers allow signals to be boosted at regular intervals, minimizing the need for costly and complex electronic regeneration systems.
Optical amplifiers, especially EDFAs, are highly efficient because they amplify the optical signal directly without converting it into electrical form. This direct amplification reduces the overall power consumption of the system, making it more energy-efficient than traditional electronic repeaters.
1550nm optical amplifiers can amplify a wide range of wavelengths, making them ideal for modern communication systems that use wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM). WDM allows multiple signals to be transmitted simultaneously over the same optical fiber, significantly increasing the capacity of fiber optic networks. The 1550nm optical amplifier can handle a broad spectrum of wavelengths, which is crucial for supporting high-bandwidth applications.
EDFAs have a low noise figure, which is essential for maintaining the quality of the amplified signal. This is particularly important in systems that require high signal-to-noise ratios (SNR), such as long-distance and high-capacity communication systems.
As 1550nm optical amplifiers can be used over long distances without requiring extensive signal regeneration, they reduce the overall cost of deploying and maintaining optical networks. Their ability to amplify signals without the need for complex and expensive equipment makes them a cost-effective solution for network providers.
1550nm optical amplifiers are primarily used in the following areas:
One of the most significant applications of 1550nm optical amplifiers is in telecommunications, where they are used in long-haul fiber optic networks. These amplifiers enable high-speed data transmission over vast distances, providing the backbone for global communication systems.
Optical amplifiers are crucial in internet backbone networks, which connect large data centers and provide high-speed internet access to users worldwide. The ability to amplify signals over long distances ensures that internet traffic can flow seamlessly without degradation in speed or quality.
1550nm optical amplifiers are also used in cable television systems to boost the strength of signals transmitted through optical fibers. By amplifying the signals, these systems can deliver high-quality video content to subscribers over long distances without significant signal loss.
WDM technology enables the transmission of multiple signals at different wavelengths over the same fiber. 1550nm optical amplifiers are critical in these systems as they amplify all the channels simultaneously, allowing for higher data capacity and more efficient use of existing fiber infrastructure.
In satellite communication systems, optical amplifiers are used in the ground station to amplify signals before they are transmitted to the satellite. The 1550nm wavelength is particularly effective for this purpose due to its low loss in fiber optic cables.
Optical amplifiers are also used in medical equipment and scientific research, where they can amplify light signals for various sensing and diagnostic applications. For example, in optical coherence tomography (OCT), 1550nm light is used to image tissues, and optical amplifiers help boost the signal strength.