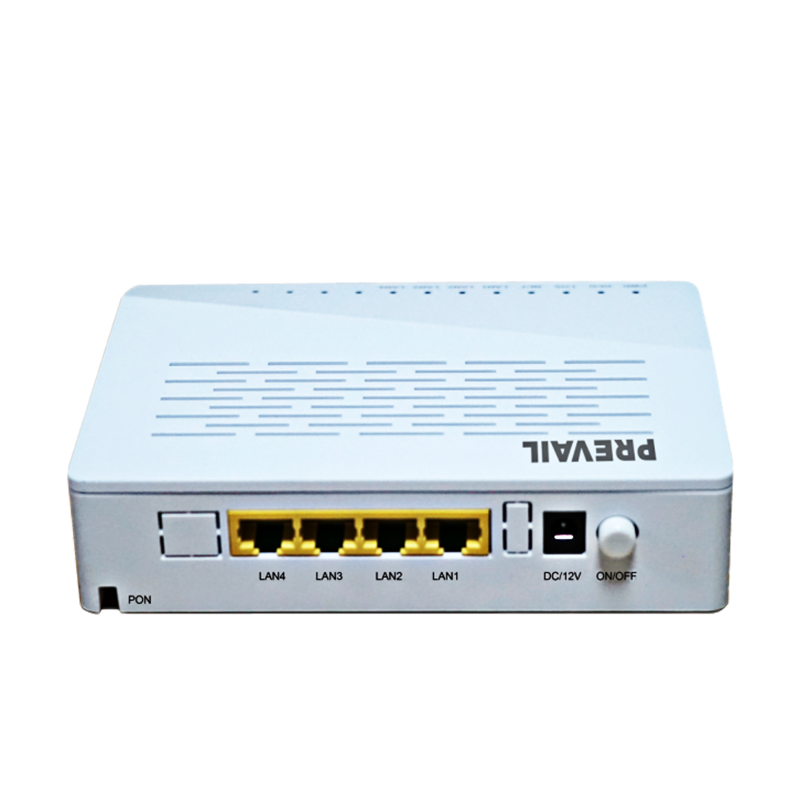
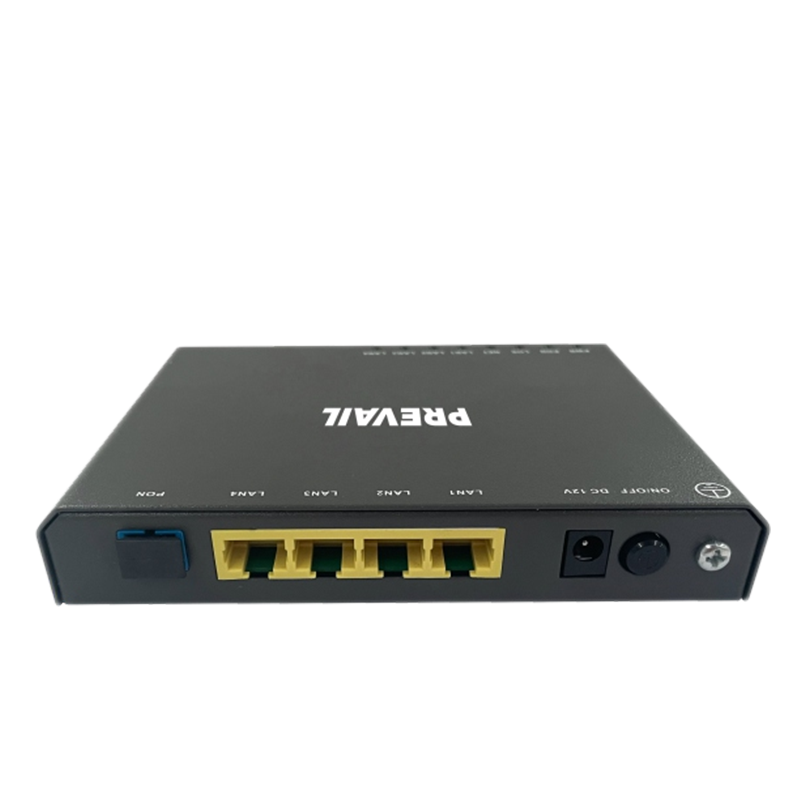
HFC transmission equipment: a key technology to promote the development of broadband networks
With the popularization of the Internet and the continuous growth of broadband demand, efficient and reliable transmission technology has become increasingly important. Among the many transmission technologies, Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial (HFC) transmission technology has become an important supporting technology for cable TV and broadband networks due to its advantages of high bandwidth, low cost and wide coverage. As a core component of this technology, HFC transmission equipment plays a vital role in the construction and operation of broadband networks. This article will explore in depth the working principle, application scenarios, technical advantages and future development trends of HFC transmission equipment.
HFC transmission technology is a combination of optical fiber communication technology and coaxial cable communication technology. It uses the high bandwidth advantage of optical fiber and the flexibility of coaxial cable to achieve long-distance and high-speed transmission of broadband signals. HFC networks are usually composed of head-end equipment, optical fiber lines, optical nodes and coaxial cables. HFC transmission equipment mainly includes the following categories:

This part of the equipment is responsible for transmitting the broadband signal generated by the head end to the optical node close to the user end through optical fiber. The main equipment includes optical transmitters, optical receivers and optical amplifiers, etc.
Optical nodes are key nodes in HFC networks, responsible for converting optical signals into electrical signals for transmission to the user end via coaxial cables. Optical node equipment usually includes optoelectronic conversion modules, amplifiers, and modems.
In the "last mile" from the optical node to the user, coaxial cable transmission equipment is responsible for transmitting broadband signals to ensure signal stability and reliability. Such equipment includes amplifiers, distributors, and filters.
HFC transmission equipment has been widely used in many fields, and its main application scenarios include:
HFC technology was first used in cable TV networks to provide transmission services for analog and digital TV signals. Through HFC networks, users can not only receive high-definition TV signals, but also enjoy value-added services such as interactive TV and video on demand.
With the development of the Internet, HFC technology has been widely used in broadband Internet access services. Using HFC transmission equipment, service providers can provide high-speed and stable broadband access to home and corporate users, supporting large-scale data transmission, online games, high-definition video and other applications.
In some areas, HFC networks are also used for telecommunications services such as voice calls and video conferencing. This application expands the service scope of HFC technology and further enhances its market value.
HFC transmission equipment is also used to build local area networks within enterprises and communities, providing shared network resources and Internet access services for multiple users.
HFC networks use the high bandwidth advantages of optical fiber to support large-scale data transmission and high-density user access. The optical fiber part provides extremely high transmission rates, while coaxial cable further improves channel capacity through frequency division multiplexing technology.
Compared with all-optical networks, HFC networks have lower construction and operation costs. The use of coaxial cable reduces the cost of network deployment, making it an economical solution acceptable to both service providers and users.
The hybrid architecture of HFC networks enables them to cover a wide range of geographic areas, including urban, suburban and rural areas. This wide coverage makes it an ideal choice for service providers in a variety of environments.
HFC transmission equipment has high flexibility and can be expanded and upgraded according to demand. By adding or upgrading equipment, service providers can easily expand network capacity to meet growing bandwidth needs.
Future development trends of HFC transmission equipment
With the continuous advancement of technology and changes in user needs, HFC transmission equipment will face more development opportunities and challenges in the future. The following are some possible development trends:
Future HFC transmission equipment may develop in the direction of full-duplex, supporting high-bandwidth transmission with symmetrical uplink and downlink. This will further improve the transmission efficiency of HFC networks and meet users' needs for high-bandwidth applications.
With the continuous evolution of the DOCSIS (Data Transmission Channel Interface Specification) standard, HFC transmission equipment will adopt the updated DOCSIS 4.0 standard. This standard will bring higher transmission rates and stronger network performance, laying the foundation for the next generation of broadband services.
Future HFC transmission equipment will integrate more intelligent functions, such as automatic configuration, fault detection and performance optimization. These functions will help improve network reliability and operational efficiency.
With the increase in environmental awareness, the design of HFC transmission equipment will pay more attention to energy saving and environmental protection. By optimizing equipment power consumption and reducing material waste, future HFC equipment will be more in line with the requirements of sustainable development.
HFC transmission equipment plays an important role in modern broadband networks. Its efficient transmission capacity, wide application scenarios and flexible scalability make it an ideal choice for service providers and users. With the continuous advancement of technology, HFC transmission equipment will play a greater role in improving network performance, reducing operating costs and meeting user needs. In the future, HFC technology will continue to lead the development of broadband networks and provide better services to global Internet users.