FTTH fiber optic receivers drive home network revolution, achieving higher speed and stability
As global broadband demand continues to grow, FTTH optical receiver as key devices in fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) networks, are gradually changing the Internet experience of homes and small businesses. FTTH technology lays optical fiber directly to users' homes, providing higher speeds, lower latency, and more stable Internet connections than traditional copper wire networks. With the widespread application of new technologies such as 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT), the market demand for FTTH fiber optic receivers is showing explosive growth and has become an important part of broadband upgrades.
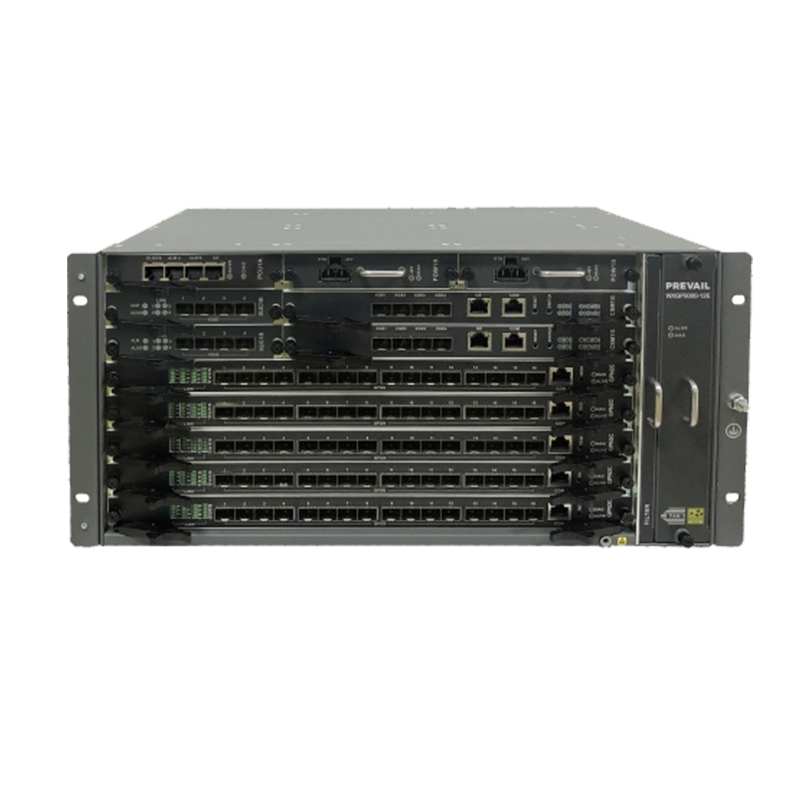
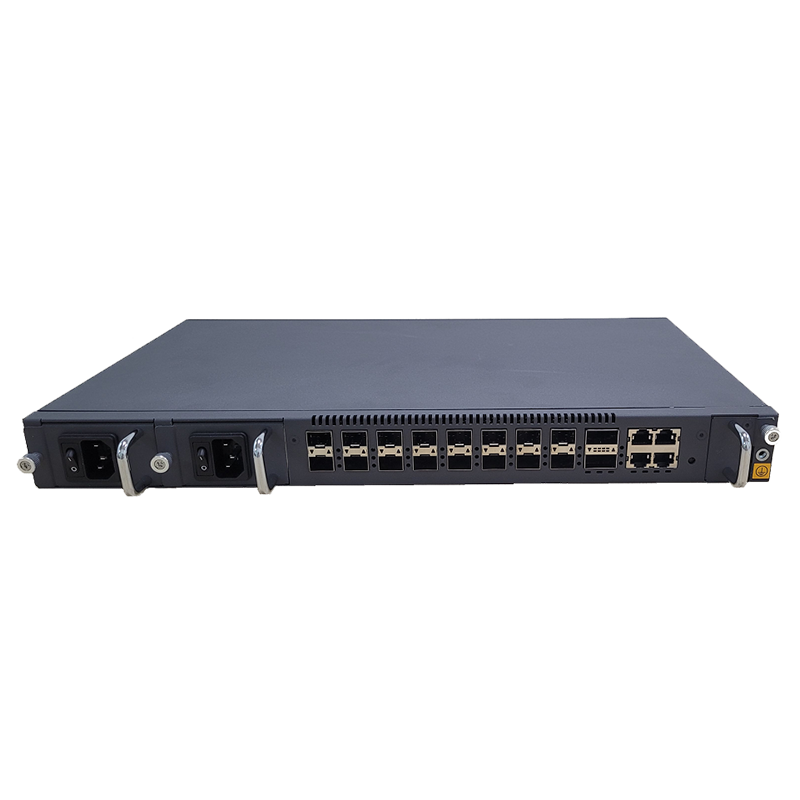
FTTH fiber optic receivers are one of the core devices in FTTH networks, responsible for converting optical signals transmitted by optical fiber networks into electronic signals, thereby supporting the connection of devices in homes or small businesses to the Internet. Compared with traditional DSL or cable networks, FTTH fiber optic receivers have higher bandwidth capacity and can carry high-speed Internet services from hundreds of megabits to several gigabits (Gbps). Its low loss characteristics allow the signal to remain stable during long-distance transmission, thereby ensuring the reliability of the network.
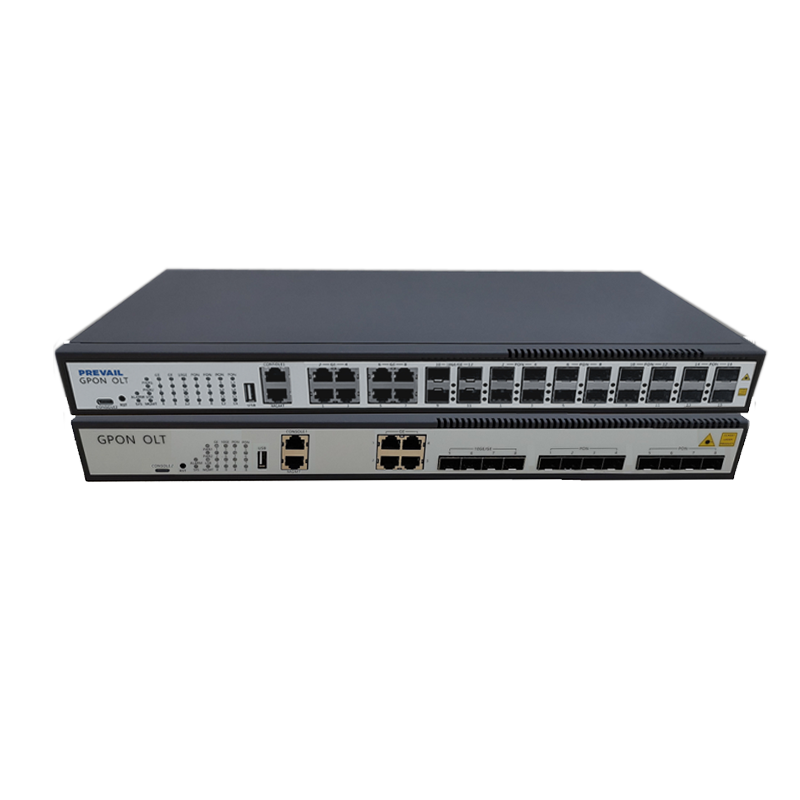
A typical FTTH system consists of an optical line terminal (OLT), an optical distribution network (ODN), and user-end equipment (ONU or ONT). FTTH fiber receivers are usually connected to ONU/ONT devices to receive optical signals transmitted from operators and convert them into electronic signals that can be used by home routers, smart devices and other devices.

The low power consumption, small size and easy installation of fiber receivers make them widely used in FTTH systems, especially suitable for the needs of homes and small businesses. In addition, as fiber networks gradually become popular around the world, the performance of fiber receivers is constantly improving, not only with larger bandwidth, but also with better anti-interference capabilities, further improving the user's Internet experience.
Globally, the wave of broadband network upgrades is in full swing. Many countries and regions have begun to regard fiber to the home as the core goal of future broadband development. For example, EU countries, the United States, Japan and China have launched large-scale FTTH deployment plans to improve the speed and stability of national Internet access. According to market research companies, the global FTTH equipment market will maintain rapid growth in the next few years, with an annual compound growth rate (CAGR) expected to reach more than 10%.
In this context, FTTH fiber optic receivers have become a key product to promote this transformation. Especially with the rise of smart homes and the Internet of Things, the number of devices connected to the Internet in homes has increased dramatically, from smart TVs, voice assistants to home security monitoring systems, all of which rely on high-speed and stable network environments. Traditional broadband access methods can no longer meet the bandwidth requirements of these devices, and FTTH fiber optic receivers can provide higher bandwidth and lower latency for home networks, greatly improving the overall user experience.
Against the backdrop of the rapid development of remote work and online education, home users' dependence on the network has further deepened. The high-bandwidth, low-latency network supported by FTTH fiber optic receivers can effectively reduce problems such as video conference freezes and online class disconnections, ensuring users' work and learning efficiency at home.
With the development of FTTH technology, the technological innovation of fiber optic receivers has continuously promoted their performance improvement. In recent years, the integration of fiber optic receivers has been greatly improved. Not only does it support higher-speed optical signal conversion, it also has compatibility with multiple network protocols and can seamlessly connect with network devices of different brands. This enables fiber optic receivers to adapt to more diverse network environments and user needs.
In order to further improve network security, some advanced FTTH optical receiver also have encrypted transmission and firewall functions, which can effectively prevent data leakage and network attacks, and protect users' privacy and information security. At the same time, with the advent of 5G networks, some FTTH fiber optic receivers have begun to support 5G backhaul technology to achieve seamless connection between fiber optic networks and wireless networks, providing users with more comprehensive network services.
In terms of energy efficiency, the power consumption of fiber optic receivers has been continuously reduced, especially in home scenarios. The low-power design not only reduces power consumption, but also extends the service life of the equipment, bringing users a more environmentally friendly and economical solution.
Although the market prospects for FTTH optical receiver are broad, there are still some challenges in its promotion process. First, the high cost of infrastructure construction, especially in remote areas, the difficulty of laying optical fiber is greater, resulting in certain restrictions on the speed of FTTH popularization. Secondly, although the technology of fiber optic receivers is becoming more and more mature, some users still need to improve their awareness and acceptance of products, especially in developing countries and regions.
With the continuous development of 5G, the Internet of Things and smart homes, the potential of the FTTH optical receiver market will be further released. The broadband strategic support of governments and the large-scale investment of operators will promote the further popularization of FTTH technology and enhance the Internet access experience of home users around the world. As the core equipment of FTTH network, fiber optic receiver will continue to play a vital role in this transformation, laying the foundation for more efficient and stable network connections.