The Rise of 1550nm Optical Transmitters: Advancing High-Speed Communication Networks
In the rapidly evolving world of optical communication, the 1550nm optical transmitter is emerging as a critical component in advancing high-speed data transmission. These devices, designed to transmit optical signals over long distances, are essential for the backbone of modern communication systems, including internet infrastructure, telecommunications, and data centers.
The 1550nm optical transmitter is an optical communication device that emits light at a wavelength of 1550 nanometers (nm). This wavelength lies in the range of infrared light and is one of the most commonly used in optical fiber communication systems. The popularity of the 1550nm wavelength is primarily due to its optimal transmission characteristics, particularly in terms of low signal loss and minimal attenuation over long distances.
In an optical communication system, the transmitter sends information as modulated light signals through optical fibers. These signals travel over vast distances, typically across cities, countries, or even continents, without significant degradation. The 1550nm wavelength is particularly well-suited for these long-distance transmissions, thanks to its low attenuation properties and high efficiency.
The Advantages of 1550nm in Optical Communication
One of the key reasons for the widespread adoption of 1550nm optical transmitters in telecommunications is the excellent performance of optical fibers at this wavelength. When light is transmitted at 1550nm, the optical fiber’s attenuation—essentially the reduction in signal strength—remains low, ensuring that data can travel over long distances with minimal signal loss. This makes 1550nm optical transmitters ideal for long-haul communication systems, which require high efficiency and reliability.
Additionally, optical fibers designed for use with 1550nm signals offer significantly higher bandwidth compared to other wavelengths. This means that large volumes of data can be transmitted simultaneously, facilitating high-speed communication that meets the increasing demands of modern applications such as cloud computing, streaming, and big data processing.
Another notable advantage of 1550nm optical transmitters is their compatibility with erbium-doped fiber amplifiers (EDFAs). EDFAs are optical amplifiers that help boost the strength of light signals as they travel through fiber optics. When used in conjunction with 1550nm optical transmitters, EDFAs enable longer transmission distances without the need for signal regeneration, which is both costly and time-consuming. This combination results in more efficient and cost-effective communication systems.
The widespread deployment of 1550nm optical transmitters has transformed a variety of industries, ranging from telecommunications to cloud services and beyond. Some of the key applications of these transmitters include:
Long-distance optical fiber communication systems rely heavily on 1550nm optical transmitters to maintain high-quality, uninterrupted service. Whether used for telephone communication, internet service, or broadband delivery, 1550nm transmitters ensure that signals travel efficiently over large distances with minimal loss, supporting the ever-growing demand for faster and more reliable data transmission.
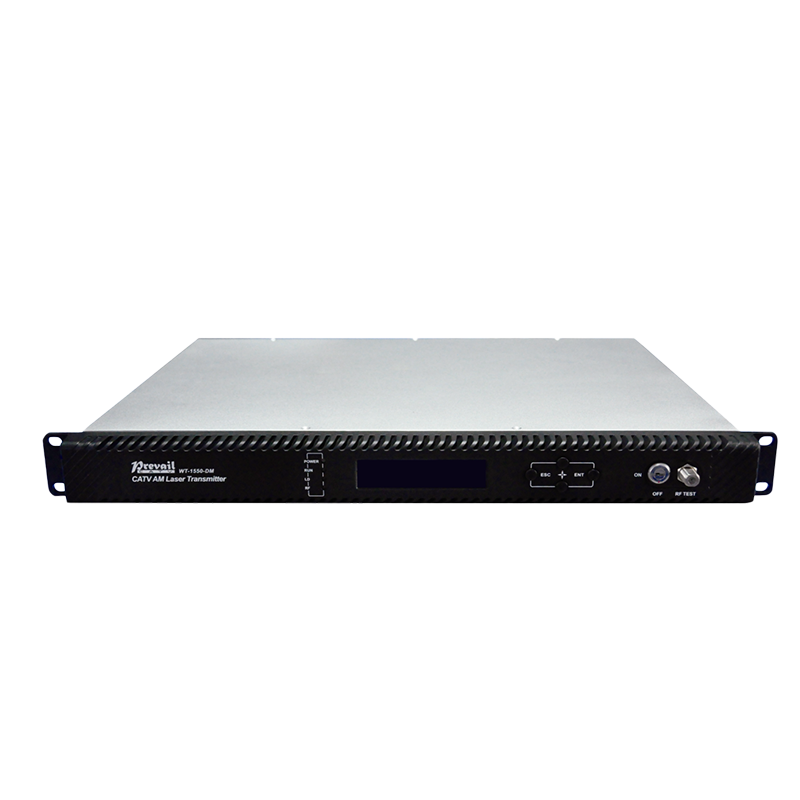

As data centers expand to meet the needs of cloud-based services, 1550nm optical transmitters are playing a vital role in facilitating rapid, high-capacity data transfer. These transmitters support high-bandwidth, low-latency communication, enabling data centers to handle large volumes of traffic and ensure smooth, seamless cloud computing experiences for end-users.
The 1550nm optical transmitter is also integral to fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) deployments, which bring high-speed internet and television services directly to consumers. By using the 1550nm wavelength, service providers can deliver ultra-fast broadband speeds and high-definition video content with minimal signal degradation.
Undersea communication cables, which form the backbone of international data transfer, rely on 1550nm optical transmitters for their long-distance, high-capacity transmission capabilities. These cables span oceans and continents, linking regions and facilitating global communication, financial transactions, and data exchange.
As demand for faster internet speeds, larger bandwidths, and more reliable communication systems continues to rise, the role of 1550nm optical transmitters will only become more critical. With the expansion of 5G networks, the need for high-speed, long-distance data transmission is becoming even more urgent, positioning the 1550nm optical transmitter as a key enabler of next-generation communication technologies.