Data Broadband Access Equipment: Enabling the Future of High-Speed Connectivity
In today’s increasingly digital world, the demand for fast, reliable, and uninterrupted internet connectivity is at an all-time high. Whether for businesses, educational institutions, or households, broadband access plays a pivotal role in ensuring that individuals and organizations can access critical information, stream content, and communicate with ease. Central to the delivery of high-speed internet is data broadband access equipment, which facilitates the connection between users and the broader telecommunications network.
These devices connect to various forms of broadband networks, including fiber-optic, cable, DSL (Digital Subscriber Line), and wireless networks, each with unique benefits and limitations. The equipment is designed to ensure data transmission is stable, secure, and efficient, while also supporting a wide range of internet services, such as video conferencing, online gaming, cloud computing, and content streaming.
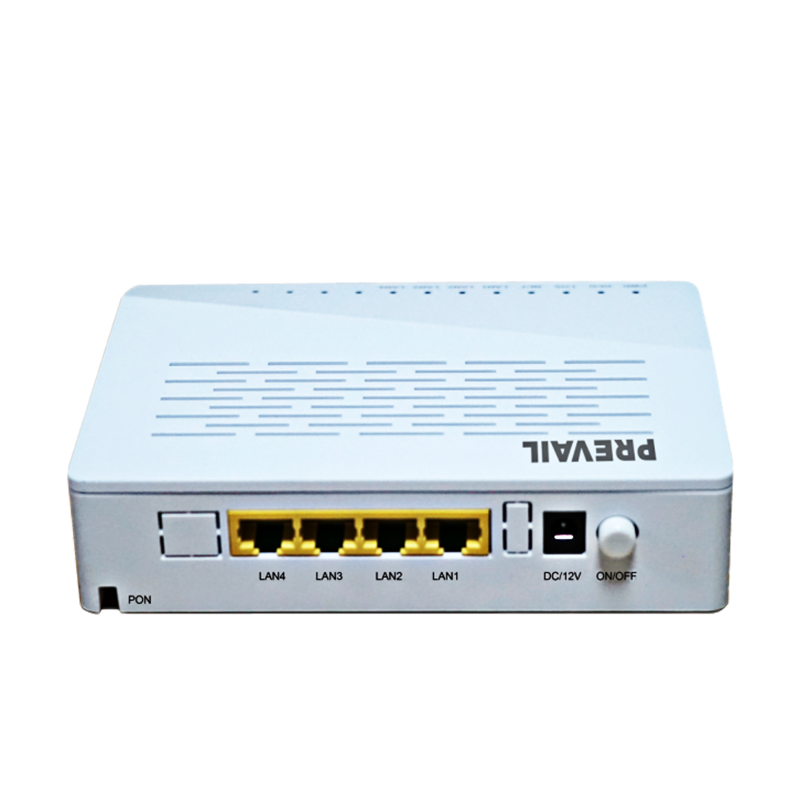
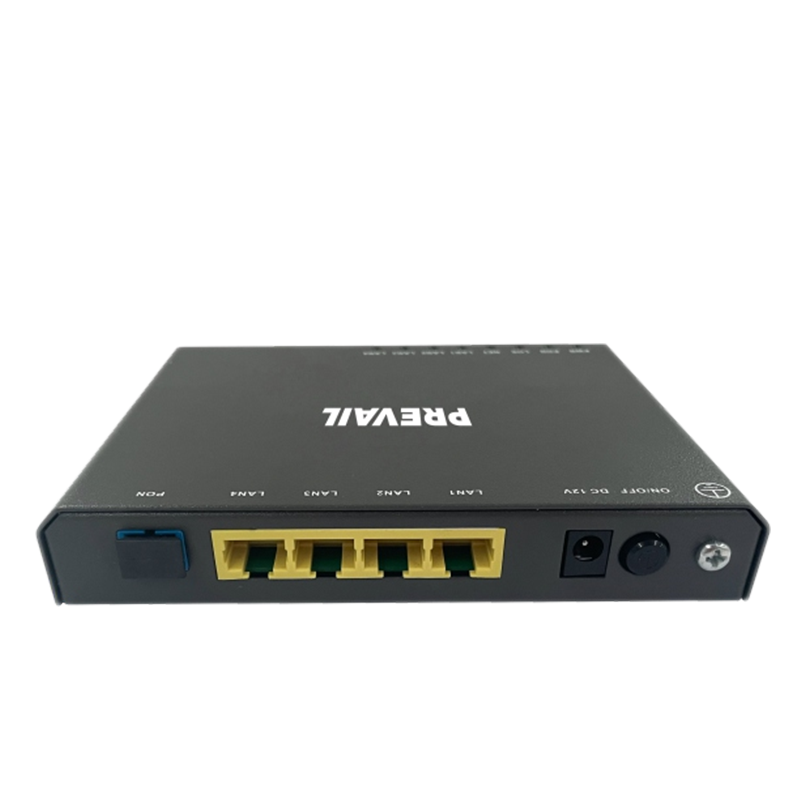
A modem (short for modulator-demodulator) is one of the most common broadband access devices. It is responsible for converting digital data from the user’s device into signals that can be transmitted over the broadband network (modulation) and converting incoming signals back into digital data (demodulation). Depending on the type of broadband connection, there are different types of modems:
Used for cable broadband connections, which deliver high-speed internet over coaxial cables.
Used for digital subscriber line (DSL) connections, which run over telephone lines.
Used for fiber-optic connections, where light signals are transmitted over optical fibers.
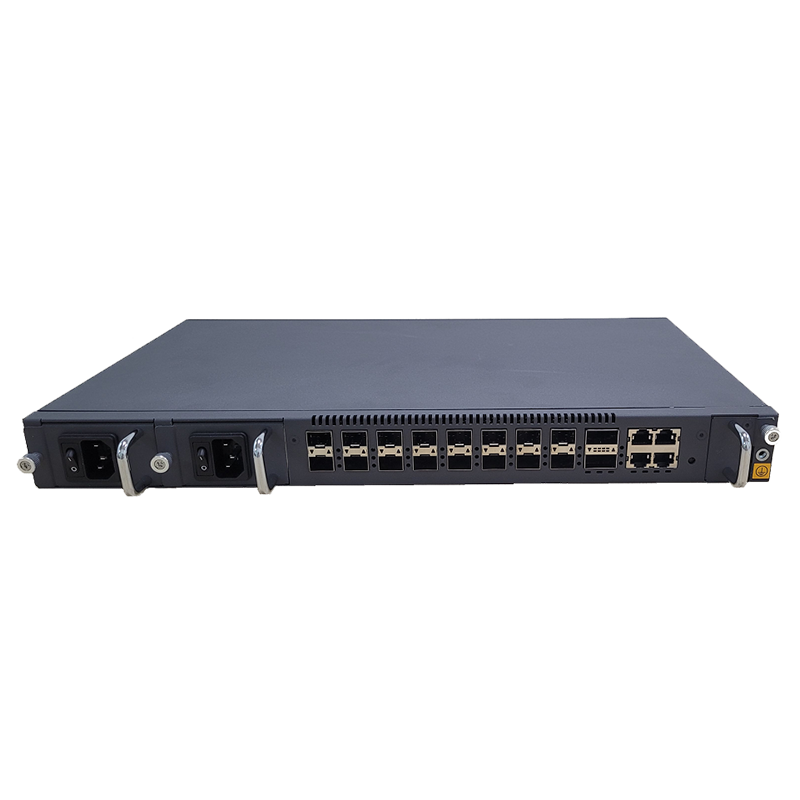
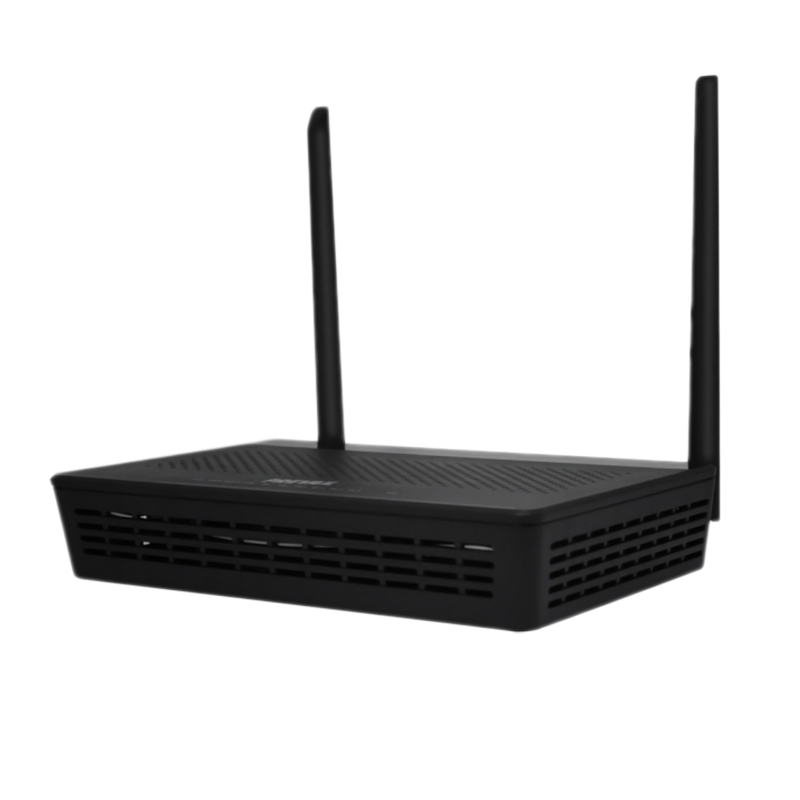
A router is responsible for directing data between the modem and devices within the local network. It routes internet traffic from the modem to various devices, such as computers, smartphones, and smart devices, connected via Wi-Fi or Ethernet cables. Modern routers are capable of providing both wireless (Wi-Fi) and wired (Ethernet) connections and often come with additional features like firewalls, security protocols, and Quality of Service (QoS) management.
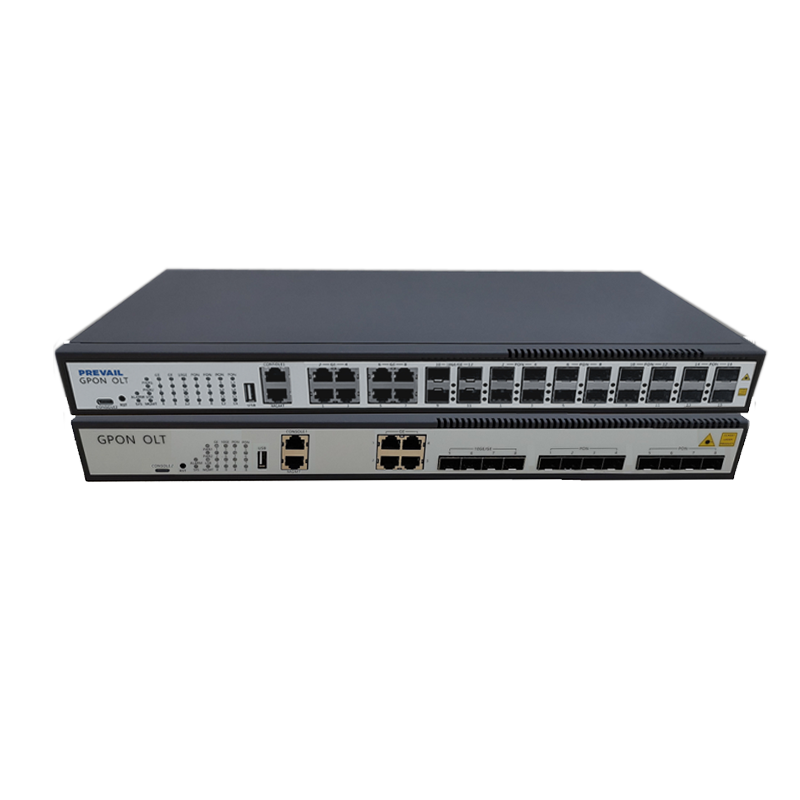
For fiber-optic broadband, ONTs serve as the end-point equipment that connects the fiber-optic network to the user’s premises. The ONT converts the optical signals received from the fiber-optic line into electrical signals, which can then be used by devices in the home or business.
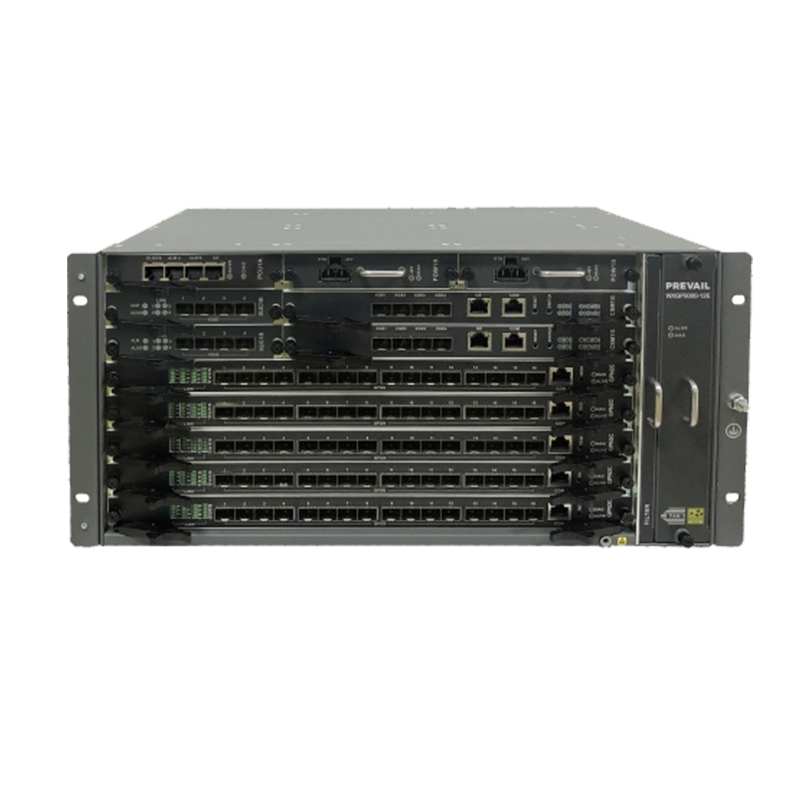
A switch is a device that connects multiple devices within a local area network (LAN), allowing them to communicate with each other. Switches play a key role in managing data traffic within a network, ensuring that data packets are sent to the correct devices.
A gateway is a more complex piece of equipment that combines the functionality of a modem, router, and sometimes a switch into a single device. It acts as the point of entry between the local network and the external internet service provider’s network, managing data traffic in both directions.
Wireless Access Points (WAPs) are devices that allow Wi-Fi-capable devices to connect to a wired network. They are used in large areas, like offices or homes with multiple floors, to extend the range and improve the signal strength of a wireless network.
Broadband access equipment plays a crucial role in providing high-speed internet access to consumers and businesses. Here are some key ways in which this equipment enhances connectivity:
One of the primary reasons for investing in modern broadband access equipment is the ability to handle faster speeds. As demand for higher data speeds grows due to more people working remotely, streaming video, and using data-heavy applications, broadband access equipment needs to support gigabit or even multi-gigabit speeds. Advanced modems, routers, and ONTs are capable of handling these higher speeds by supporting the latest technologies, such as DOCSIS 3.1 for cable internet or GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Networks) for fiber-optic broadband.

Modern broadband access equipment is designed to minimize downtime and ensure a stable connection. Devices such as routers and switches manage network traffic efficiently, preventing congestion and ensuring that data is delivered in a timely manner. Additionally, many devices feature built-in redundancy options, such as backup power sources or multiple communication channels, to minimize service interruptions.
With the increasing use of cloud-based applications, video conferencing tools, and IoT (Internet of Things) devices, broadband access equipment must be capable of supporting a wide range of services. High-performance routers and ONTs enable these applications by providing fast and stable connections with sufficient bandwidth to support multiple devices and data streams simultaneously.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, ensuring the security of broadband networks has become more important than ever. Modern broadband access equipment often comes with built-in security features, such as firewalls, encryption, and VPN (Virtual Private Network) support, which help protect users from online threats and unauthorized access to their network.
With the growth of smart homes, connected devices, and business networks, broadband access equipment must be scalable to meet the growing demands of consumers and enterprises. Many modern routers and switches support features like mesh networking, allowing users to expand their network easily by adding additional access points or routers.