Can you tell me more about fiber optic switches?
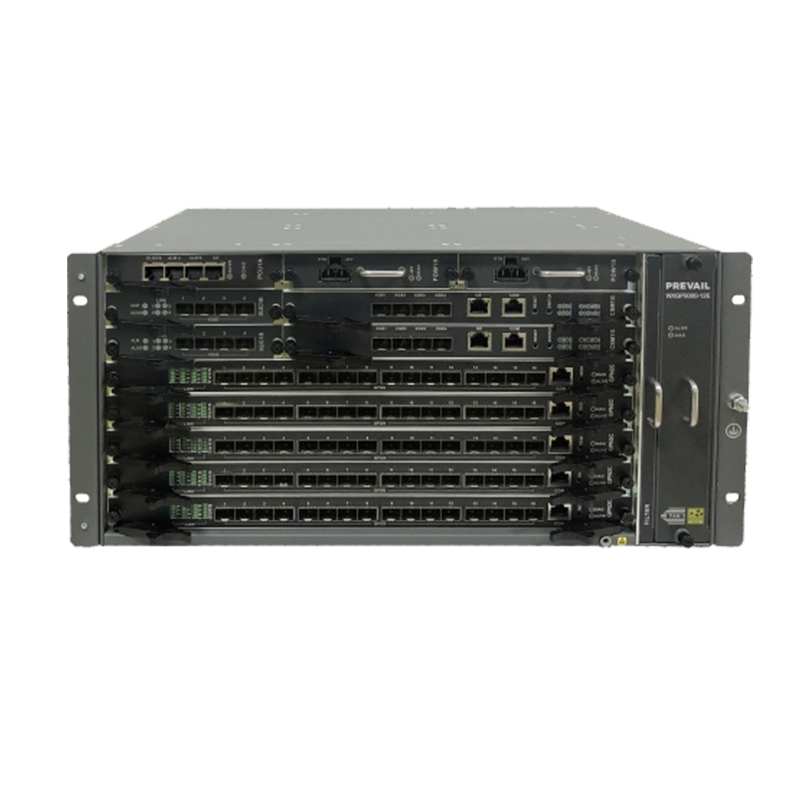
A fiber optic switch is a network device used to transmit data in a fiber optic network. It plays a key role in computer networks and is used to exchange, route and forward data. Here are some details about fiber optic switches:
Working principle: Fiber optic switches transmit data through optical fiber transmission media, use photoelectric conversion technology to convert digital signals into optical signals, and transmit them through optical fibers. At the receiving end, the fiber optic switch converts the optical signal back into a digital signal.
Data exchange: The fiber optic switch determines the destination of the data based on the destination address (such as MAC address) in the data packet, and forwards the data packet to the corresponding target device. It has multiple ports, each of which is connected to a device or other network device to enable the exchange of data.
Routing function: Some advanced fiber optic switches also have routing functions that can make forwarding and routing decisions based on the IP address of the device. Such switches are called Layer 3 switches and are capable of more complex network topology and routing control.
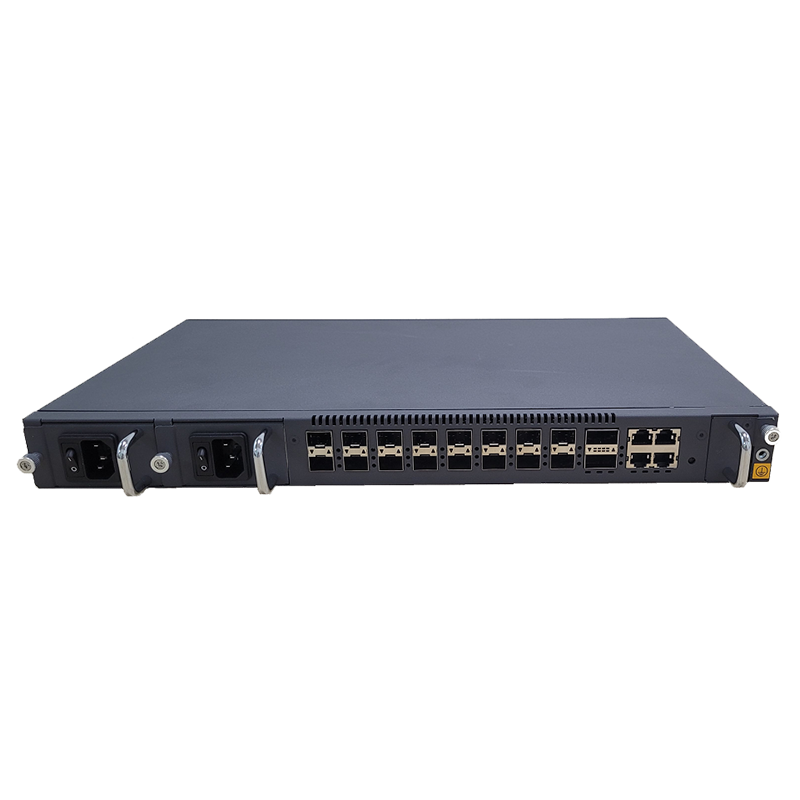
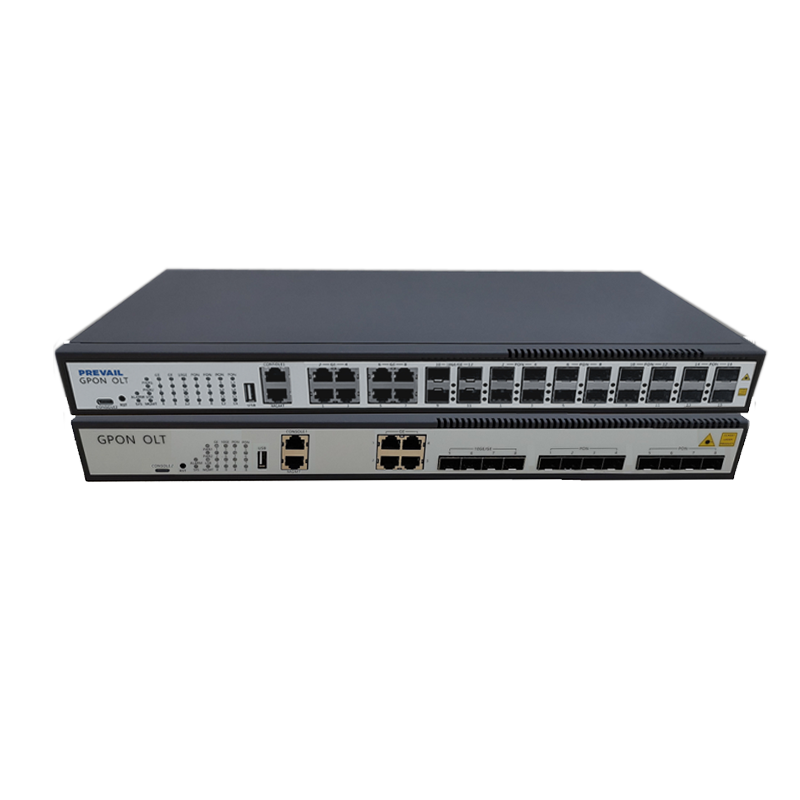
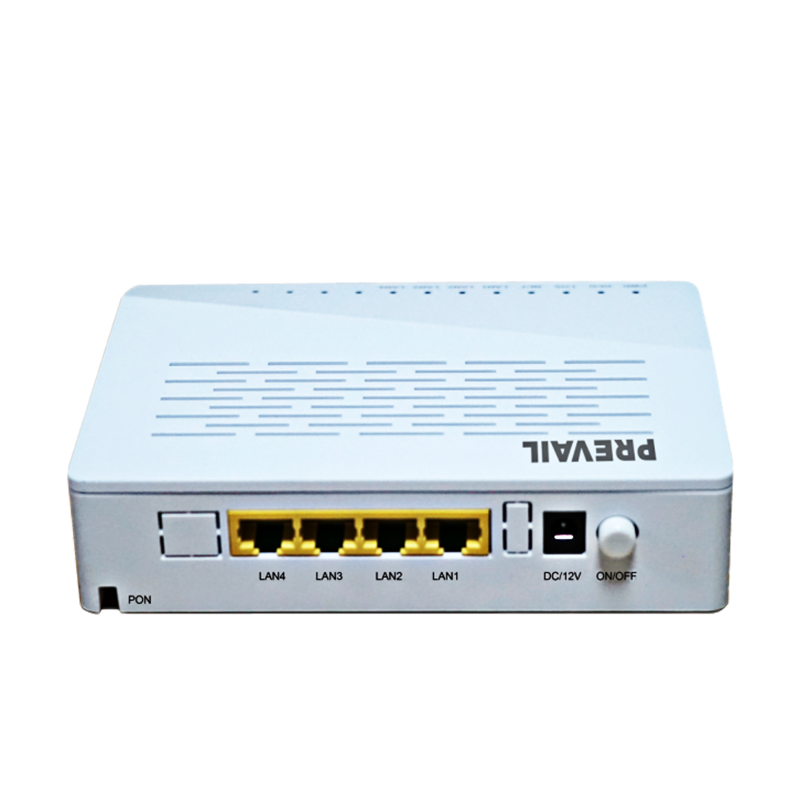
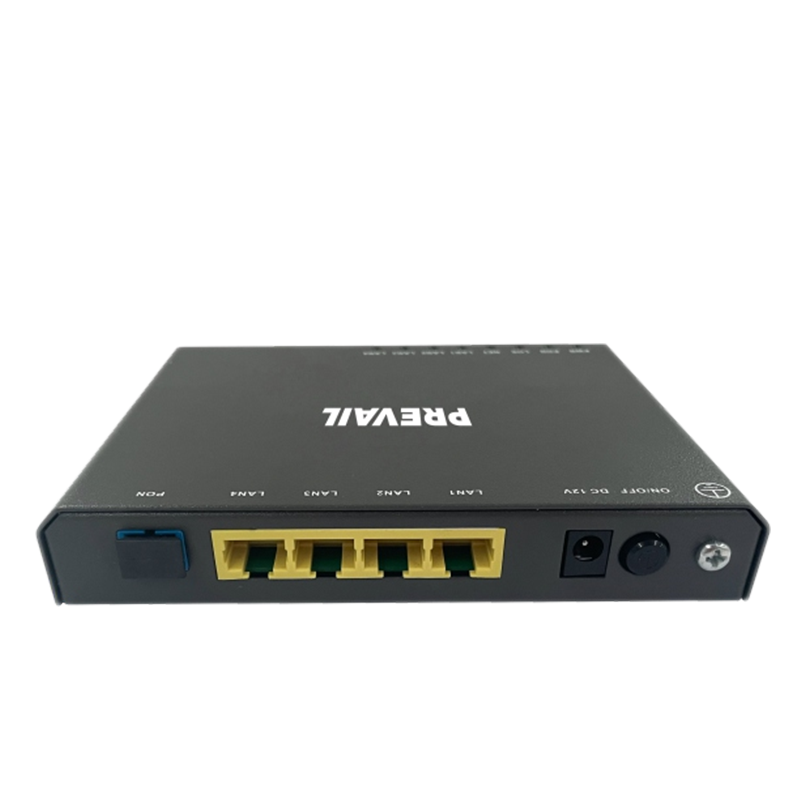
Port type: Fiber optic switches usually have multiple ports for connecting fiber optic equipment or other network devices. Common fiber optic switch port types include fiber optic ports (such as SC, LC, ST, etc.), Ethernet ports (such as RJ-45), and Gigabit Ethernet ports (such as SFP or SFP+).
Network management: Fiber optic switches usually provide network management functions, allowing administrators to configure and monitor the operating status of the switch. Management functions may include virtual LAN (VLAN) configuration, port speed settings, traffic control, security settings, and more.
Scalability: Fiber optic switches support multiple ports and high-bandwidth data transmission, so they have good scalability. They can be connected to other switches or routers to form larger network architectures.
Performance and speed: Fiber optic switches have high-speed data transmission capabilities and low latency. They enable high-bandwidth data exchange and are suitable for applications requiring high-speed and large-volume data transmission, such as data centers, enterprise networks and cloud computing environments.
Security: Fiber-optic switches usually provide some security features, such as access control lists (ACLs), port security, and user authentication. These features help protect the network from unauthorized access and cyberattacks.
Fiber optic switches play an important role in modern computer networks. They provide high-speed, reliable and secure data transmission, support complex network topology and routing control, and meet network applications of different sizes and needs.